
KNOWLEDGE BASE Value Added Tax in The UK
The information on this page was current at the time it was published. Regulations, trends, statistics, and other information are constantly changing. While we strive to update our Knowledge Base, we strongly suggest you use these pages as a general guide and be sure to verify any regulations, statistics, guidelines, or other information that are important to your efforts.
Brexit Update:
Since the UK officially left the European Union on January 31, 2020, the relationship between the two has evolved and continues to be shaped by the ongoing implementation of the withdrawal agreement.
Key Dates:
-
January 31, 2020: UK officially left the EU and entered a transition period that ended on December 31, 2020.
-
December 31, 2020: The transition period ended, and the UK fully exited the EU single market and customs union.
-
January 1, 2021: The UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement came into effect, outlining the post-Brexit relationship between the two entities.
-
2023/2024 Current: The UK and EU are still navigating the ongoing implementation and potential revisions of their post-Brexit relationship.
It's crucial for businesses operating in either the UK or the EU to stay informed about the latest developments and adjust their operations accordingly.
Value Added Tax in The UK
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a broad-based consumption tax levied on the sale of all supplies of goods and services in the United Kingdom. VAT is paid every time a customer buys a taxable good or service from a VAT-registered business. Suppliers essentially act as VAT collection agents.
To whom and what does the Value Added Tax apply?
Value Added Tax applies to you if you are a VAT-registered business that supplies goods or services to customers. You must register for VAT with HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) if your business’ VAT taxable turnover is more than £85,000. You can register voluntarily if your turnover is below this number, unless everything you sell is exempt. The primary reason you would consider voluntary registration is to reclaim the VAT you incur through your own business purchases and expenses, i.e., the VAT you pay when purchasing supplies for your business.
How do I comply with VAT?
VAT-registered businesses must charge VAT on their goods and services. All VAT-registered businesses must report the amount of VAT they charged and the amount of VAT they paid to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). This is done through a VAT Return, which is usually submitted every 3 months. VAT-registered businesses may reclaim the VAT they have paid on business-related goods and services.
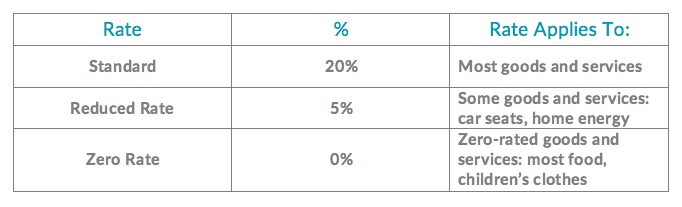
There are three VAT rates and it is your responsibility to ensure you charge the correct rate.
-
Standard Rate: Most goods and services are standard rate. Unless a good or service is classified as reduced rate or zero rate, you should charge the standard rate.
-
Reduced Rate: Reduced rate depends on the good or service being provided and the circumstances of the sale.
-
Zero Rate: Zero rate means the goods or services are still VAT taxable, but the rate your charge your customers is 0%. All zero-rate transaction must still be accounted for and reported on your tax return.
You will find detailed information on the registration process here. Online registration is done through HMRC.
Here is a list of reduced-rate or zero-rated goods and services.
VAT Rates For Goods and Services
If a transaction is standard, Reduced, or Zero-rated, you must:
-
charge the correct rate of VAT;
-
calculate the VAT if a single price is shown that either includes or excludes VAT;
-
show the VAT information on your invoice;
-
record the transaction in your VAT account (a summary of your VAT); and
-
show the amount on your VAT Return.
You cannot charge VAT on items that are exempt or “out of the scope” of VAT. As a VAT-registered business, you can sell goods or services to charities at the zero or reduced rate. It is your responsibility to check and confirm that the charity is eligible and apply the correct rate. You may be charge VAT on discounts and deals. You do not have to pay VAT on free samples, if they meet certain criteria.
VAT on Digital Services
As of January 1, 2015, the VAT rules for place of supply change in the European Union (EU) for sales of digital services from businesses to consumers.
![]()
If your business sells digital services to consumers in EU members states, you must charge VAT at the rate due in the consumer’s country.
What is considered a digital service to which VAT applies? To which digital service providers does VAT apply?
Digital services for purposes of determining VAT include, but are not limited to:
-
broadcasting
-
telecommunications
-
e-services, such as video on-demand, downloadable applications (apps), music downloads, gaming, e-books, software or software updates, downloadable trainings, tutorials, images, etc.
VAT on digital services applies to the sale of those digital services to consumers, it does not apply if you sell only to other businesses.
Keeping records
All VAT-registered businesses must:
-
keep records of sales and purchases;
-
keep a separate summary of VAT called a VAT account; and
-
issue correct VAT invoices.
You must keep VAT records for at least six years (10 years if you use the VAT MOSS Service). You can keep VAT records on paper, electronically, or as part of a software program, e.g., a book-keeping system. All records must be accurate, complete, and readable.
![]()
HMRC can visit your business to inspect your records keeping and can charge you a penalty if your records are not in order.
For specific requirements of VAT invoicing and record retention, see the Information Commissioner’s Office’s website.
List of Reduced-Rate and Zero-Rated Goods and Services
KNOWLEDGE BASE Value Added Tax in The UK


